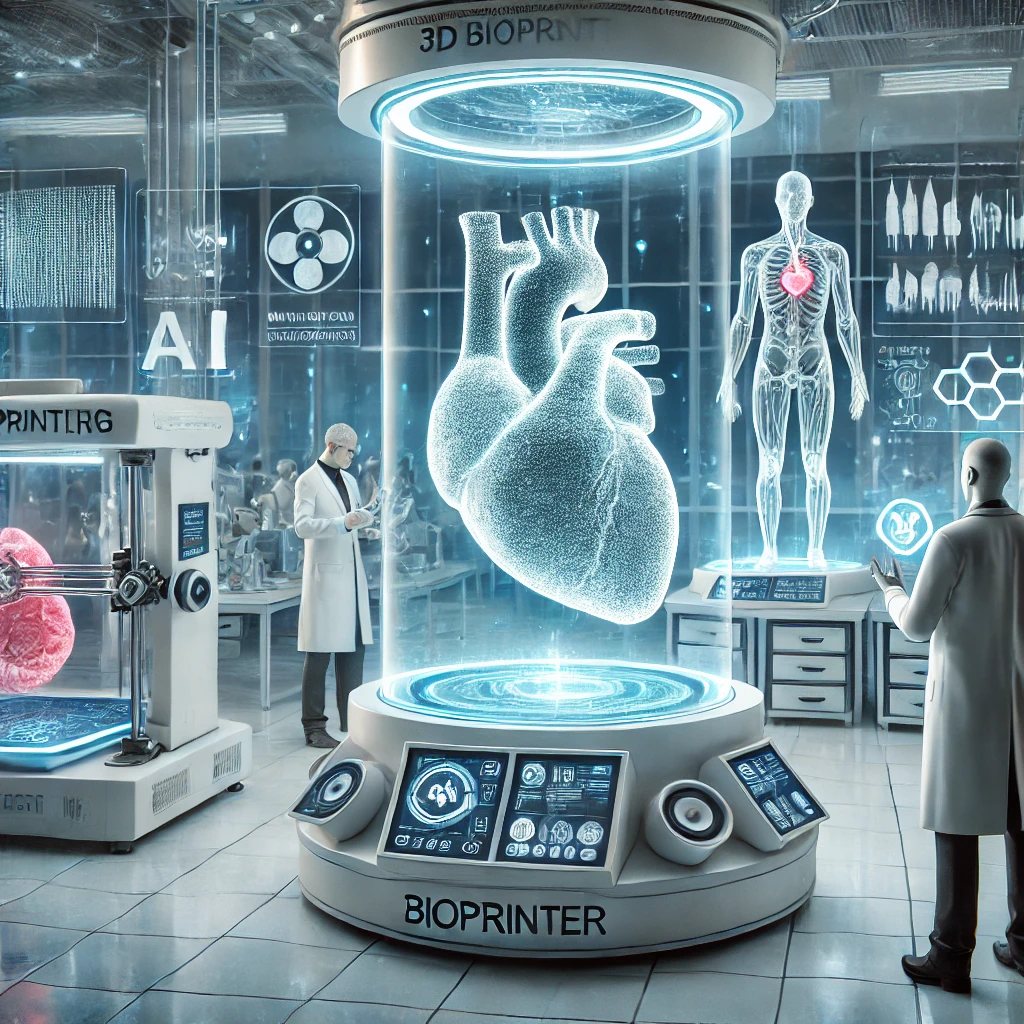
3D Bioprinting: The Game-Changer in Organ Transplants and the Future of Medical Innovation
Introduction: A Future Where Organs Are Printed, Not Donated
Imagine a world where waiting lists for organ transplants no longer exist. Where a patient in need of a new heart, liver, or kidney doesn’t have to rely on a donor but instead gets a custom-built organ bioprinted from their own cells.
This is not a sci-fi dream—this is the reality that 3D bioprinting is bringing to modern medicine. As we move towards a future where technology and biology merge, scientists are developing functional, lab-grown organs that could one day replace traditional transplants.
With groundbreaking advancements in biomaterials, artificial intelligence (AI), and regenerative medicine, 3D bioprinting is poised to disrupt the healthcare industry forever.
🚀 But how does it work?
🧬 Can we actually print a functional human heart?
💉 How soon will bioprinted organs replace traditional transplants?
Let’s dive deep into the world of bioprinting and its potential to revolutionize healthcare.
What is 3D Bioprinting?
3D bioprinting is an advanced tissue engineering technology that uses bio-inks, living cells, and biomaterials to create human tissues and organs layer by layer. It works like traditional 3D printing, but instead of plastic or metal, it prints with biological materials to mimic real human tissues.
How Does 3D Bioprinting Work?
1️⃣ Cell Collection & Bio-Ink Preparation:
- Patient’s own stem cells are extracted and cultivated.
- These cells are mixed with hydrogels, proteins, and other biomaterials to create a printable “bio-ink.”
2️⃣ Digital Blueprinting & 3D Modeling:
- AI and imaging technologies (like MRI & CT scans) create a digital 3D model of the organ needed.
- The model is customized to the patient’s anatomy for a perfect fit.
3️⃣ Layer-by-Layer Printing:
- The 3D bioprinter deposits bio-ink, building tissue structures layer by layer.
- Special bioreactors help cells grow and integrate.
4️⃣ Tissue Maturation & Vascularization:
- Printed tissues are placed in a controlled incubator where they develop and form networks of blood vessels, nerves, and functional tissues.
5️⃣ Transplantation & Testing:
- The bioprinted organ is tested for functionality and compatibility before being transplanted.
🔥 This method promises to make organ transplantation safer, faster, and more accessible than ever before.
3D Bioprinting & The Future of Organ Transplants
1. Ending the Organ Donor Crisis
📉 The Problem:
- Millions of patients worldwide are waiting for organ transplants.
- Organ shortages lead to thousands of deaths every year.
- Even when a donor is found, immune system rejection remains a risk.
🛠️ How 3D Bioprinting Solves This:
- Custom-built organs using a patient’s own cells eliminate rejection risks.
- Unlimited supply of organs, reducing waiting times.
- Patients can receive a perfectly matched, bioengineered organ in weeks instead of years.
✅ Success Story: Scientists have already bioprinted functional liver tissues, and researchers are working on full-scale liver and kidney transplants.
2. Printing Functional Human Hearts, Kidneys & Livers
🔬 Scientists are successfully printing:
✅ Heart tissue patches for patients with heart disease.
✅ Bioprinted kidney tissues that filter toxins like real kidneys.
✅ Miniature livers that function similarly to natural organs.
💡 Breakthrough: In 2019, researchers at Tel Aviv University bioprinted a tiny human heart with blood vessels—proving that full-scale heart bioprinting is possible in the near future.
3. Cornea & Skin Bioprinting for Burn Victims
🦾 3D-printed corneas could restore vision to millions.
🔥 Bioprinted skin grafts are already helping burn victims.
💊 Wound healing accelerators using printed tissue are being tested.
🔬 Scientists predict that bioprinted skin will soon replace traditional skin grafts for burn victims and cosmetic surgery patients.
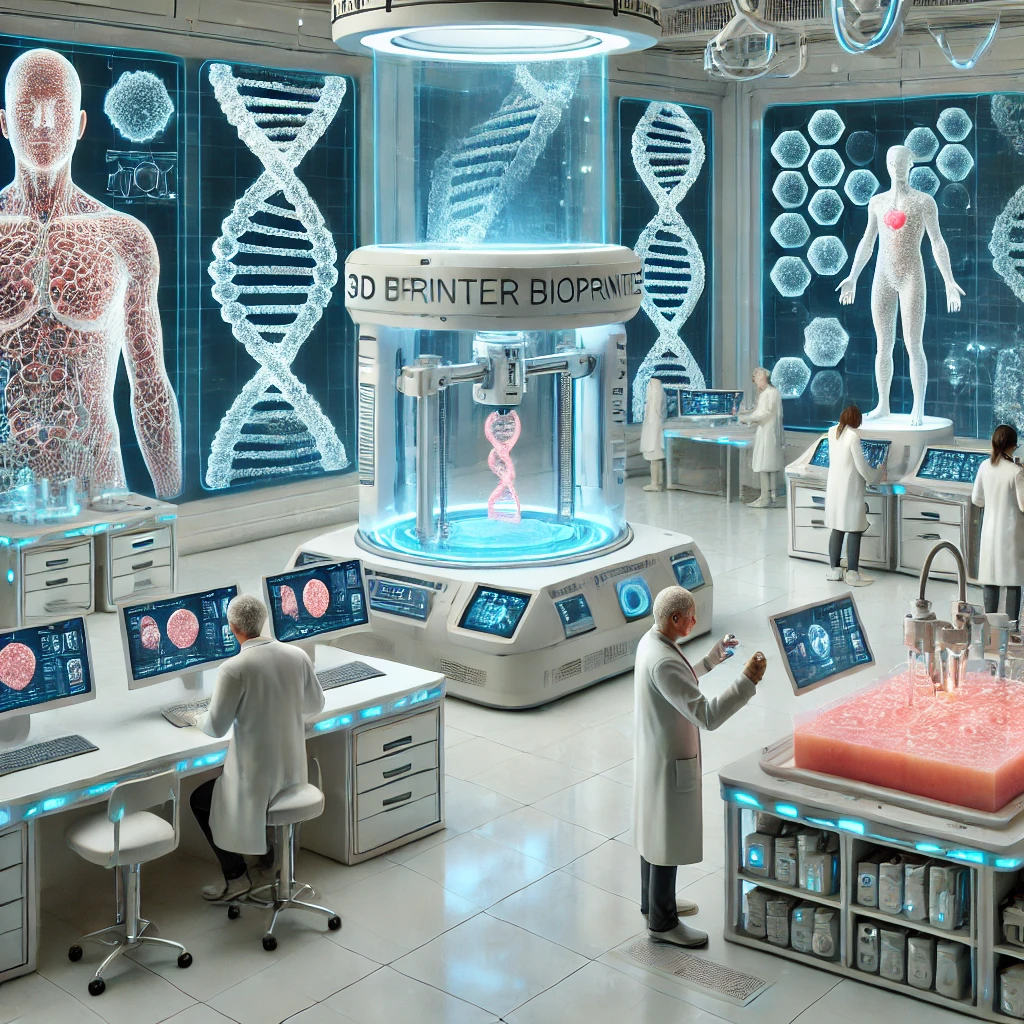

Beyond Transplants: The Medical Innovations of 3D Bioprinting
🧪 1. Drug Testing & Personalized Medicine
- No more relying on animal testing—bioprinted human tissues allow realistic drug testing.
- Pharmaceutical companies are already using bioprinted liver tissues to test medications.
🎯 2. Cancer Research & Disease Modeling
- 3D bioprinted tumors allow scientists to study cancer in real-time.
- Helps researchers test treatments on lab-grown tumors before human trials.
💉 3. AI-Powered Precision Medicine
- AI and machine learning analyze patient data to create personalized bioprinted tissues.
- Doctors can custom-print tissues for specific genetic profiles.
Challenges & Limitations of 3D Bioprinting
🔴 1. Can We Print Large Organs Like Lungs & Kidneys?
- Challenge: Full-sized organs require complex vascular networks (blood vessels, nerves).
- Solution: Scientists are developing bioprinted blood vessels to support organ function.
💰 2. High Costs & Scalability Issues
- Challenge: Bioprinting is expensive, and widespread use is limited.
- Solution: Advances in automation, AI, and mass production will reduce costs.
🛑 3. Regulatory & Ethical Concerns
- Challenge: Is it ethical to print human body parts?
- Solution: Governments and medical organizations are setting strict ethical guidelines.
The Future of 3D Bioprinting: How Close Are We?
📅 Experts predict:
- 2025-2030: Bioprinted tissues for drug testing & disease modeling will become mainstream.
- 2030-2040: Full-sized, transplantable bioprinted hearts and kidneys may become reality.
- 2050: On-demand organ printing could be available in hospitals worldwide.
🚀 NASA is already experimenting with 3D bioprinting in space to advance regenerative medicine in zero gravity.
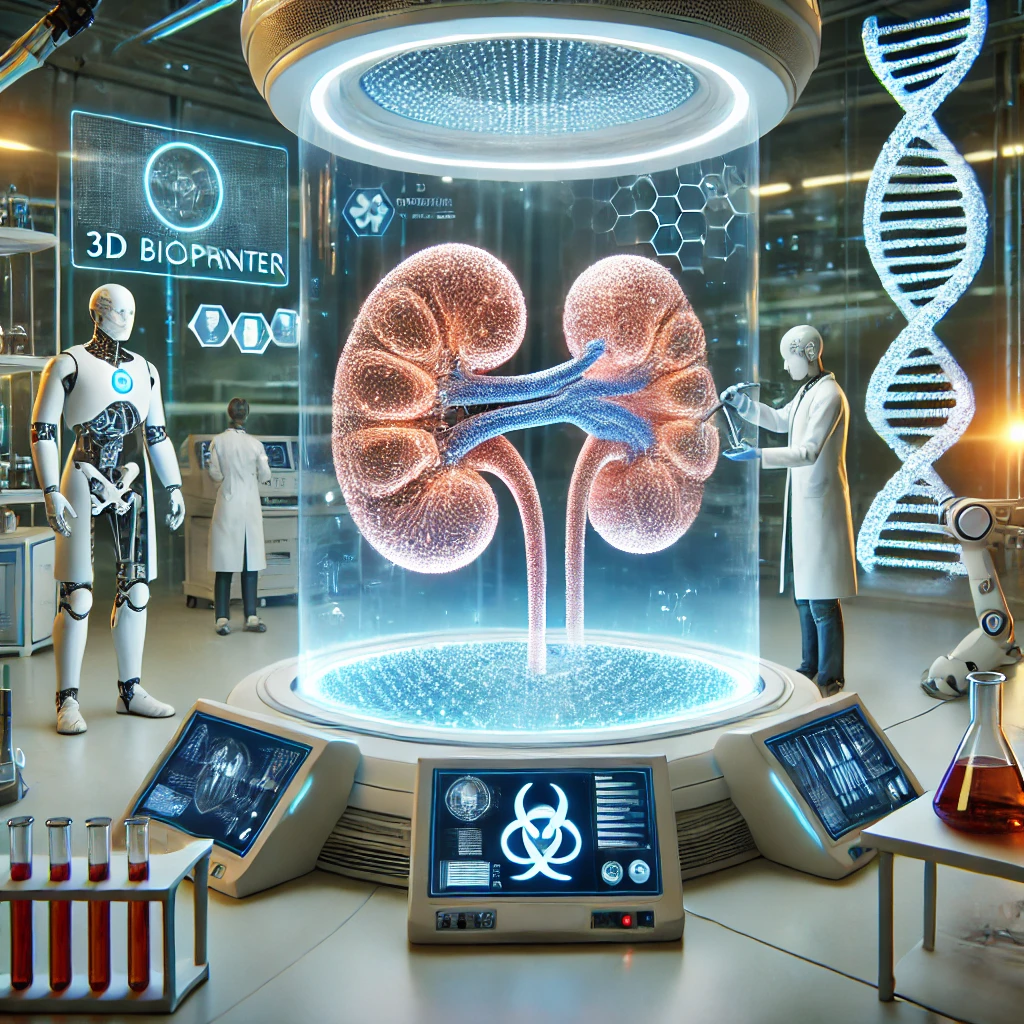

Conclusion: The Future of Medicine is Being Printed
3D bioprinting is not just an idea—it’s happening now. As scientists push the boundaries of tissue engineering, AI, and regenerative medicine, we are moving closer to a future where:
✅ No one dies waiting for an organ transplant.
✅ Personalized, rejection-free organs are printed on demand.
✅ Medical research and drug testing are revolutionized by lab-grown tissues.
👨⚕️ The age of organ printing is near—are we ready to embrace this medical revoluti